Abstract
Background: Rituximab (RTX) is commonly used to treat Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM). Treatment options are limited for patients (pts) who fail rituximab therapy. Single-agent ibrutinib (ibr) is highly active in WM and is approved in the United States and Europe for WM. In the phase 3 iNNOVATE study, ibr plus RTX resulted in significantly longer PFS and higher response rates vs RTX alone, both among TN and previously treated pts with WM (Dimopoulos MA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2018). Previous reports from the open-label, single-agent substudy showed sustained responses and a manageable toxicity profile in RTX-refractory WM, with a median follow-up of 18.1 mo (Dimopoulos MA, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2016). Follow-up data from both the randomized portion (median follow-up of 30.4 mo) and substudy (median follow-up of 38.7 mo) of iNNOVATE are presented.
Methods: Pts had confirmed, symptomatic WM requiring treatment. Pts in the randomized portion (Arms A and B) with prior RTX therapy required a response (≥MR) to their last RTX-based regimen. Pts were randomized to daily 420 mg ibr (Arm A; IR) or placebo (Arm B; R) plus RTX (375 mg/m2/week IV at weeks 1-4 and 17-20). In Arm C, pts who failed to achieve ≥MR or relapsed <12 mo of their last RTX-containing therapy received daily 420 mg ibr until PD/unacceptable toxicity. Endpoints included PFS, response rates, OS, hemoglobin (Hb) improvement, time to next treatment (TTnT), pt-reported outcomes (PROs) and safety.
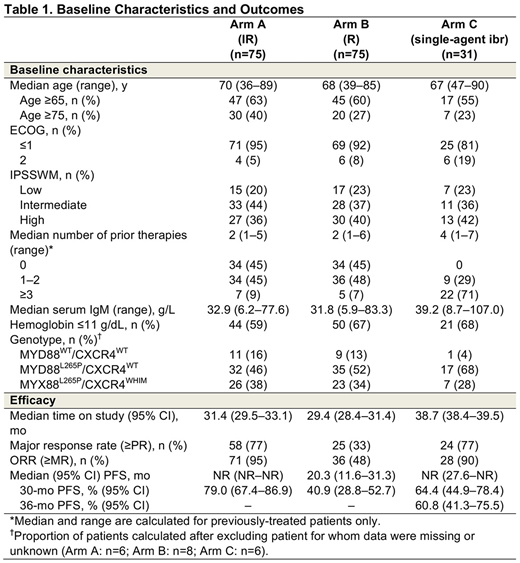
Results: A total of 150 pts were randomized to Arms A and B (n=75/arm; Table 1). Median age was 69 y. High IPSSWM was reported in 38% of pts; 45% of pts were treatment naïve. With prolonged follow-up and a median duration of treatment of 29.5 mo with IR and 15.5 mo with R, investigator-assessed major response rates (≥PR) were 77% with IR vs 33% with R (P<0.0001); ORRs (≥MR) were 95% vs 48% (P<0.0001), respectively. With continued IR treatment, 27% of pts achieved a VGPR compared to only 3% in the R arm. Major responses with IR stayed robust independent of MYD88/CXCR genotype, with time to major response of 1.8, 2.9, and 5.7 mo for MYD88L265P/CXCR4WT, MYD88L265P/CXCR4WHIM, and MYD88WT/CXCR4WT, respectively. Median investigator-assessed PFS was not reached (NR) with IR vs 20.3 mo (95% CI: 11.6-31.3) with R (HR=0.219 [0.122-0.393]; P<0.0001); estimated 30-mo PFS was 79% vs 41%. Importantly, among pts receiving IR, 30-mo PFS estimates did not show any major differences among the different genotypes. The 30-mo OS estimate was 93% with IR vs 90% with R; 31 pts on R crossed over to IR after IRC-confirmed PD. Treatment with IR was ongoing in 73% of pts; the most common reasons for discontinuation of ibr were disease progression and pt withdrawal of consent (9% each); 35% of pts who received R were in response follow-up after the interim analysis. The AE profile in the IR arm was consistent with previous reports. Overall, grade ≥3 AEs occurred in 61% of pts in both arms. Incidence of grade ≥3 AEs was 53% during the first 12 months of treatment in the IR arm and increased 8% with longer follow up. Serious AEs occurred in 43% of IR pts vs 33% of R pts. Similarly, incidence of serious AEs was 39% during the first 12 months of treatment with IR and increased 4% with longer follow up.
In Arm C, 31 pts received single-agent ibr (Table 1). Median age was 67 y. Most (71%) pts had ≥3 prior therapies; all patients were RTX-refractory and 90% had prior treatment with cyclophosphamide. High IPSSWM was reported in 42% of pts. With longer follow-up, median investigator-assessed PFS was NR (95% CI: 27.6-NR); estimated 36-mo PFS was 61%. Major response rate by investigator assessment was 77% and ORR was 90%. The estimated 36-mo OS was 84%. Improved Hb level was seen in 71% of pts. Treatment was ongoing in 52% of pts. Median duration of ibr treatment was 37.0 mo, with no major hemorrhagic or atrial fibrillation events reported. Grade ≥3 AEs occurred in 74% of pts and 39% had serious AEs. No fatal AEs were reported.
Conclusions: IR showed continued superiority over R, in treatment-naïve and previously treated pts with WM, regardless of genotypic factors. Similarly, in heavily pretreated, RTX-refractory pts with follow-up >3 y, single-agent ibr was highly active and response improved over time. Alone or in combination, ibr had a manageable safety profile and no new safety signals were identified with longer follow-up.
Buske:Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding. Tedeschi:Gilead: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Trotman:Beigene: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; PCYC: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Jassen: Research Funding. García-Sanz:Spanish Government: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Hospira: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Amgen Inc.: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses. MacDonald:Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Lundbeck: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria. Leblond:Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Speakers Bureau; Sandoz: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Herbaux:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Tam:Beigene: Honoraria, Other: Travel funding; Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Travel funding; Gilead: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria; Beigene: Honoraria, Other: Travel funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Palomba:Seres: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties; Juno: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties; Merck: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Therakos: Consultancy. Matous:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Shustik:Amgen: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Kastritis:Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Genesis Pharma: Consultancy; Prothena: Consultancy. Treon:Johnson & Johnson: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; BMS: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding. Lih:Abbvie: Employment, Equity Ownership; Abbvie/Pharmacyclics: Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses. Li:Pharmacyclics: Employment; Abbvie: Equity Ownership; BMS: Equity Ownership; Pfizer: Equity Ownership; Abbott: Equity Ownership; Amgen: Equity Ownership; Gilead: Equity Ownership; Biogen: Equity Ownership; Celgene: Equity Ownership; Medivation: Equity Ownership; Merck: Equity Ownership; Exelixis: Equity Ownership; Juno: Equity Ownership; Isis: Equity Ownership; Aduro: Equity Ownership; Merrimack: Equity Ownership. Salman:Pharmacyclics LLC: Employment, Equity Ownership; Abbvie: Equity Ownership. Graef:Abbvie: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Pharmacyclics: Employment, Other: Leadership, Patents & Royalties. Dimopoulos:Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.